A search box is probably one of the most common UI elements around, and I think there is no need to explain its purpose anymore. Whether it’s about a website or a web application, to increase user experience for it, you may want to add a stylish search box.
Today, you will learn how to create a nice CSS3 search box using pseudo-elements.
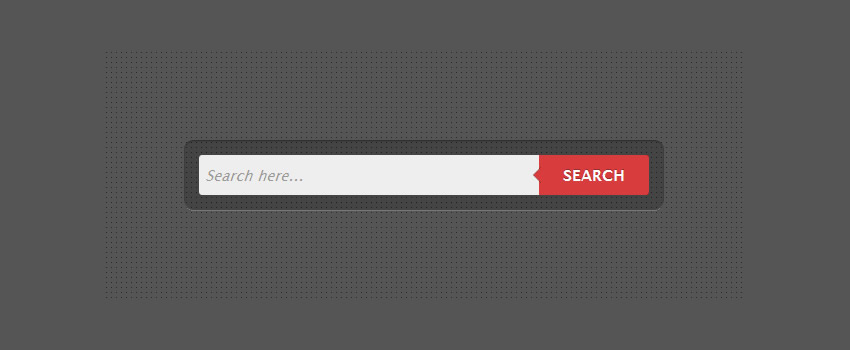
The HTML
As you can see below, the markup is minimal and easy to understand:
<form class="form-wrapper cf">
<input type="text" placeholder="Search here..." required>
<button type="submit">Search</button>
</form>
You may have noticed the HTML5’s specific attributes like placeholder and required, here’s a short description:
- placeholder– Basically, this attribute shows a text in a field until the field is focused upon, then it just hides the text.
- required– This specifies that the current element is a required part of a form submission.
HTML5 also brought us a new value for the type attribute: type="search". Though, because of cross browser inconsistency, I decided to skip it for now.
Quick Tip
HTML elements like img and input have no content, therefore, a pseudo-element like :before will not render any arrow for our search button.
My solution was to use the button type="submit" element instead of casual input type="submit". This way, we can preserve the submitting form on ENTER key functionality.
The CSS
Below you can find the necessary styles for our demo:
Clear Floats
.cf:before, .cf:after{
content:"";
display:table;
}
.cf:after{
clear:both;
}
.cf{
zoom:1;
}
Form Elements
Prefixed properties like -moz-box-shadow weren’t included, I just wanted to keep the following code clean. Though, they are included in the demo example.
/* Form wrapper styling */
.form-wrapper {
width: 450px;
padding: 15px;
margin: 150px auto 50px auto;
background: #444;
background: rgba(0,0,0,.2);
border-radius: 10px;
box-shadow: 0 1px 1px rgba(0,0,0,.4) inset, 0 1px 0 rgba(255,255,255,.2);
}
/* Form text input */
.form-wrapper input {
width: 330px;
height: 20px;
padding: 10px 5px;
float: left;
font: bold 15px 'lucida sans', 'trebuchet MS', 'Tahoma';
border: 0;
background: #eee;
border-radius: 3px 0 0 3px;
}
.form-wrapper input:focus {
outline: 0;
background: #fff;
box-shadow: 0 0 2px rgba(0,0,0,.8) inset;
}
.form-wrapper input::-webkit-input-placeholder {
color: #999;
font-weight: normal;
font-style: italic;
}
.form-wrapper input:-moz-placeholder {
color: #999;
font-weight: normal;
font-style: italic;
}
.form-wrapper input:-ms-input-placeholder {
color: #999;
font-weight: normal;
font-style: italic;
}
/* Form submit button */
.form-wrapper button {
overflow: visible;
position: relative;
float: right;
border: 0;
padding: 0;
cursor: pointer;
height: 40px;
width: 110px;
font: bold 15px/40px 'lucida sans', 'trebuchet MS', 'Tahoma';
color: #fff;
text-transform: uppercase;
background: #d83c3c;
border-radius: 0 3px 3px 0;
text-shadow: 0 -1px 0 rgba(0, 0 ,0, .3);
}
.form-wrapper button:hover{
background: #e54040;
}
.form-wrapper button:active,
.form-wrapper button:focus{
background: #c42f2f;
outline: 0;
}
.form-wrapper button:before { /* left arrow */
content: '';
position: absolute;
border-width: 8px 8px 8px 0;
border-style: solid solid solid none;
border-color: transparent #d83c3c transparent;
top: 12px;
left: -6px;
}
.form-wrapper button:hover:before{
border-right-color: #e54040;
}
.form-wrapper button:focus:before,
.form-wrapper button:active:before{
border-right-color: #c42f2f;
}
.form-wrapper button::-moz-focus-inner { /* remove extra button spacing for Mozilla Firefox */
border: 0;
padding: 0;
}
That’s all!
I hope you liked this tutorial and I’m looking forward to hearing your thoughts about it. Thank you for reading!
Related Topics
Top